In the Web3 world, users are not a monolithic traffic pool. They exist on a dynamic spectrum ranging from “Newcomers — Actives — Contributors — Core Users.”
To make growth sustainable, projects must answer two critical questions: Who are the most valuable people to cultivate? And how do we design differentiated incentives for these specific cohorts?
TaskOn integrates traditional CRM frameworks with on-chain behavior, points tiers, and task chain mechanisms to form a repeatable Web3 User Operations Map. Let’s deconstruct this system and see how it drives actual growth in the wild.
I | Why Does Web3 Need User Segmentation?
Web3 users exhibit a “High Instability Trinity”:
- High Liquidity: They join anytime, and they leave just as fast.
- High Sensitivity: Even minor changes in incentive structures immediately impact behavior.
- High Heterogeneity: The value gap between a new user and a heavy participant is massive.
In such an ecosystem, if you apply a one-size-fits-all incentive strategy, your token budget will get drained rapidly without retaining any high-quality users.
The goal of segmentation is simple: Allocate limited resources to the users with the highest compound effects.
II | The TaskOn User Segmentation Model
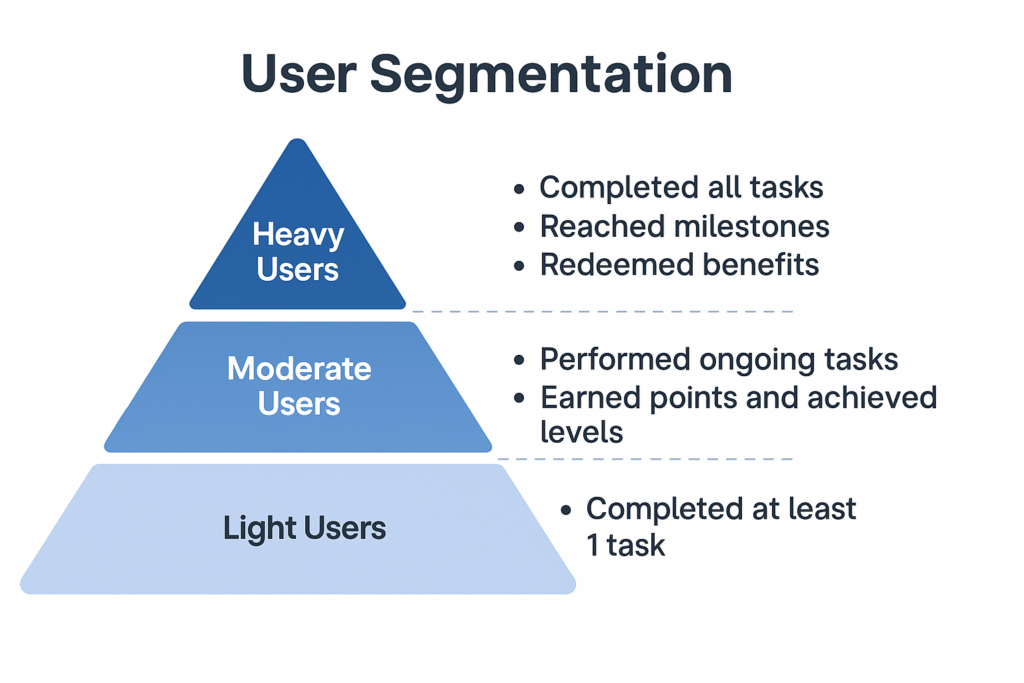
How do we scientifically grade users? TaskOn combines user behavior with task modules to categorize users into four core layers:
1) Newcomers
- Behavioral Traits: First registration, first signature, first follow, first participation.
- Corresponding Modules:
- Low-barrier Quests (Follow/Join/Visit)
- Initial Points
- “Smart Task” → Automated verification
- Goal: Complete the first real interaction (MVA – Minimum Viable Action).
2) Actives
- Behavioral Traits: Multi-day participation, repetitive task completion.
- Corresponding Modules:
- DayChain (Continuous check-ins)
- TaskChain (Basic tasks)
- Weekly themed events
- Goal: Shift behavior from “One-off” to “Continuous,” powering up the points ecosystem.
3) Contributors
- Behavioral Traits: Submitting content, trading, governance participation, completing advanced on-chain tasks.
- Corresponding Modules:
- TaskChain (Deep/Advanced tasks)
- Milestone (Auto-claim based on progress)
- Higher Points Multipliers
- Goal: Cultivate “Compound Interest” users (Do more → Get more).
4) Core Users
- Behavioral Traits: High contribution, strong social influence, stable retention, multi-cycle participation.
- Corresponding Modules:
- High Levels (Level 4–5)
- Benefits Shop (High-tier perks: WL / Promo Codes / Time-limited Privileges)
- Leaderboard (Top-tier visibility)
- Goal: Turn scarce users into a community moat.
> Note: In Community Level design, you can reference rating standards to specify different upgrade curves, benefits, and matching task gradients.
III | Incentive Models: Light / Mid / Heavy Structure
To ensure incentives are not wasted, leaked, or unsustainable, TaskOn establishes a three-tier intensity system:
(1) Light Incentives: Attracting New Users (Newcomers)
- Format:
- Follow / Join tasks
- Micro-Points
- Lucky Wheel (Raffle tickets)
- Newcomer Welcome Pack
- Goal: Lower the barrier for the user’s first action.
(2) Mid Incentives: Retaining the Actives
- Format:
- Streak Rewards (DayChain)
- Weekly Task Rewards
- Mid-tier Points + Redemption Vouchers (Lucky Ticket)
- Content Interaction Rewards
- Goal: Strengthen the reason to return.
(3) Heavy Incentives: Reserved for Contributors & Core Users
- Format:
- WL (Whitelists) / NFTs
- Trading Fee Discounts
- Gas Vouchers
- Referral Privileges
- High-Level Roles/Identity
- Partner Benefits
- Goal: Elevate the value of staying.
IV | User Operations Map: How TaskOn Drives Strategic Decisions
A mature Web3 project can use TaskOn’s user operations map to answer three key questions:
Q1: Which layer is the user in? (Behavior Data × Task Data)
TaskOn automatically records: task completion counts, consecutive participation days, completed on-chain Tasks, Point Level changes, and referral behavior. This data segments users automatically, eliminating guesswork.
Q2: What is the next step for this user layer? (Task Path)
TaskOn’s TaskChain allows you to design different behavioral paths for different tiers:
- New User → Complete MVA
- Active User → Maintain streaks
- Contributor → Complete advanced on-chain tasks
- Core User → Compete on the Leaderboard
Q3: How are incentives distributed? (Rights & Tokens)
Benefit Shop and Level permissions make incentives more precise:
- Points Redemption → Distinguishes active users
- Level Gating → Curbs Sybil/farming behavior
- Milestone Rewards → Rewards true contributors
- Premium Benefits → Retains high-value users
This allows operations teams to scientifically control costs while boosting growth efficiency.
V | Synergy with TaskOn CRM Modules: Achieving “Intelligent User Growth”
TaskOn’s user segmentation isn’t isolated; it synergizes with the entire CRM system:
- Points → Records behavioral value
- Level → User identity ladder
- Milestone → Auto-triggers stage-based rewards
- Benefit Shop → The benefits hub
- Leaderboard → Social incentivization
- Referral → Identity-driven fission
The Formula: CRM × User Segmentation × Incentive Structure = A Complete Growth Flywheel.
Conclusion: User Segmentation is Critical Infrastructure for Web3 Growth
Web3 growth isn’t about piling up vanity metrics; it’s about guiding different types of users along distinct growth paths.
TaskOn utilizes modular tools to turn this logic into a repeatable “Growth Operating System.” This enables projects to Attract, Activate, Retain, Convert, and Propagate, ultimately building a user structure that is long-term, high-quality, and driven by compound effects.